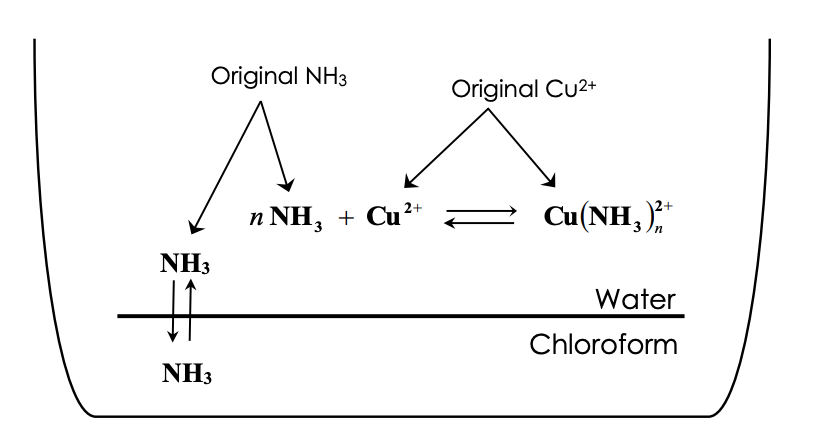
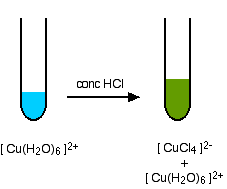
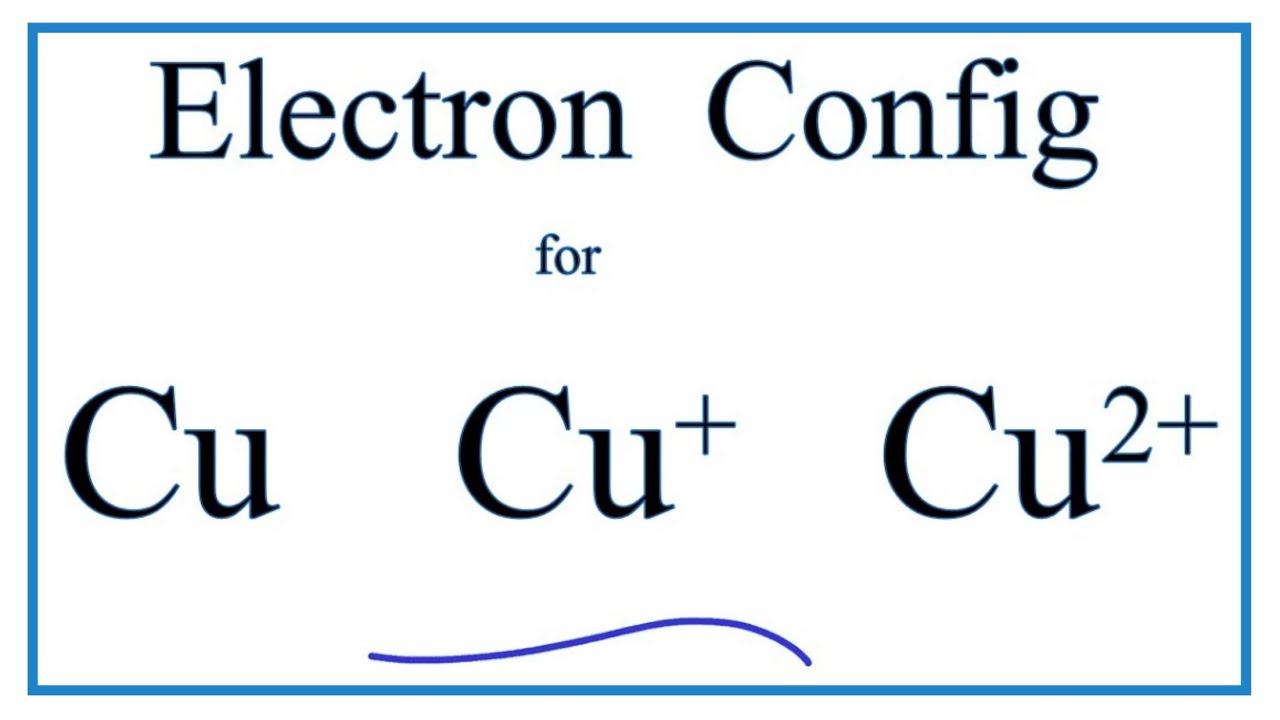
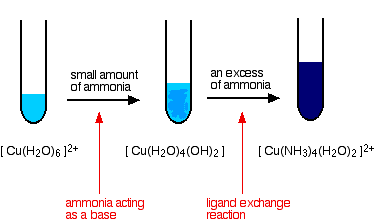
Copper Cu transition metal Chemistry copper(I) Cu+ copper(II) Cu2+ ion complex ions ligand substitution compounds redox chemical reactions principal oxidation states +1 +2 GCE AS A2 IB A level inorganic chemistry revision

Colorimetric Detection of Copper(II) Ions Using Schiff‐Base Derivatives - Aydin - 2020 - ChemistrySelect - Wiley Online Library
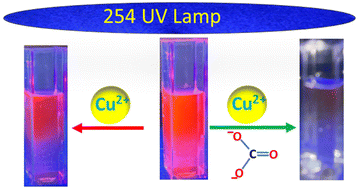
CO32− ion-induced Cu2+ ion determination using DPA capped-LaF3:Eu3+ nanocrystals - Journal of Materials Chemistry C (RSC Publishing)

SOLVED: The product solubility constant for copper (I) iodide is 1.1X 10-12 When 0.40 M HCN is added to this ionic salt; forming the complex ion, Cu(CN) 2 with a product formation constant
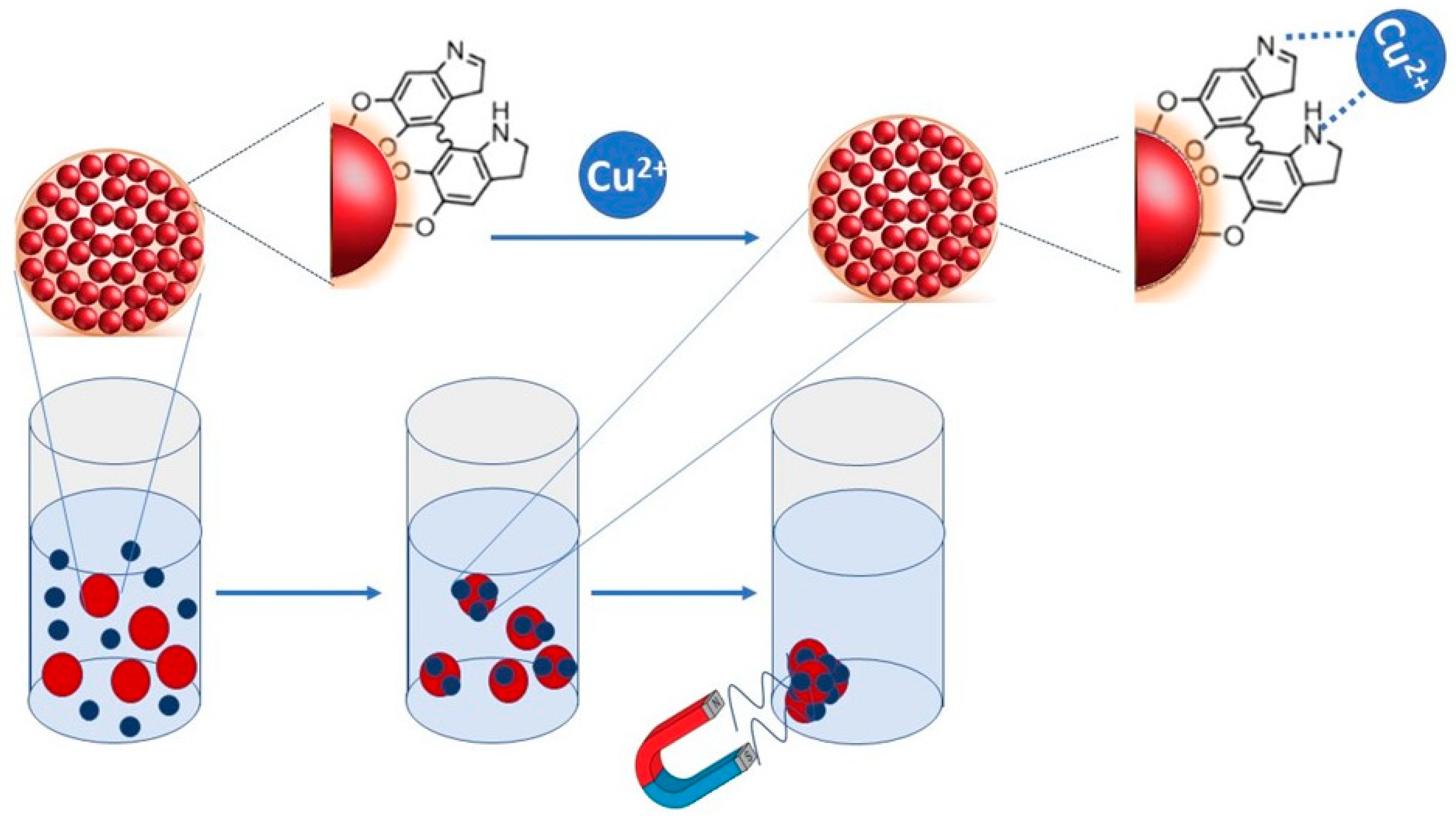
Materials | Free Full-Text | Synthesis and Characterization of SPIONs Encapsulating Polydopamine Nanoparticles and Their Test for Aqueous Cu2+ Ion Removal
![In an excess of NH(3(aq.)),Cu^(2+) ion form a deep blue complex ion [Cu (NH(3))(4)]^(2+) having formation constant K(f)=5.6xx10^(11). Calculate the concentration of Cu^(2+) in a solution prepared by adding 5.0xx10^(-3) mole of CuSO(4) In an excess of NH(3(aq.)),Cu^(2+) ion form a deep blue complex ion [Cu (NH(3))(4)]^(2+) having formation constant K(f)=5.6xx10^(11). Calculate the concentration of Cu^(2+) in a solution prepared by adding 5.0xx10^(-3) mole of CuSO(4)](https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/ss/web/355853.jpg)
![For a complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]^2 + : For a complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]^2 + :](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/1731528_b11046ad9936443990f5efe5a262d1e8.png)
.jpg)